Everything you need to know about warehouse storage
Stock organisation and management are essential factors in ensuring a company’s optimum level of both productivity and profitability. As such, the storage of goods plays a key role in this success. Poorly thought-out or inadequate warehousing can lead to loss of time, additional costs, and a drop in the quality of the products stored. This makes it crucial to choose from the different types of storage systems available, the one that is most suitable for your logistics centre and your needs. Discover the 4 main solutions available along with the criteria you need to consider determining the most appropriate storage system for you.
4 different types of warehouse storage
There are 4 different types of warehouse storage systems: Storage shelving, storage racking, automated systems, and storage for specific objects.
1. Storage shelving
Commonly used in warehouses, storage shelving is a product storage solution that offers great flexibility and easy access to items. There are three main types.
Heavy Duty Shelving
Fixed to the floor or mounted on rails, these shelves are mainly used to store heavy and bulky items for use in a variety of environments including warehouses, factories and stockrooms.

Medium Duty shelving
Usually made of steel, these permanent shelves are fixed to the floor or walls of the warehouse. They are often used to store light to medium-heavy items (e.g. office supplies).

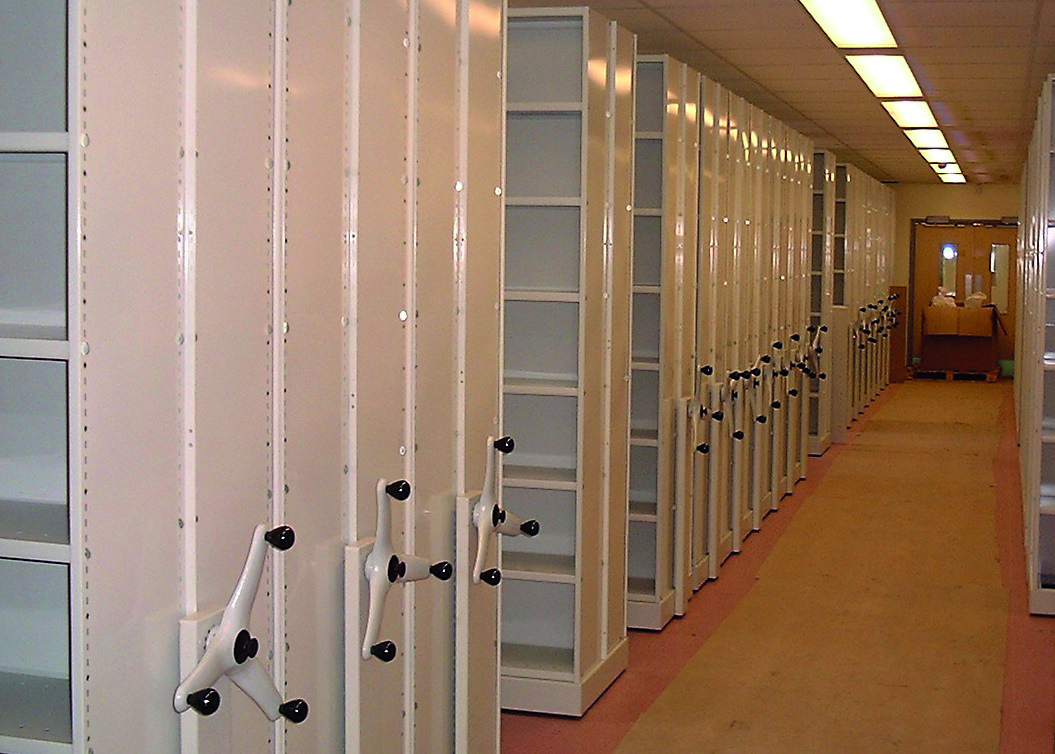
Mobile shelving
Attached to a rail system, the boards used in these shelves can slide sideways to optimise the storage area. This storage system is often used to support voluminous or irregularly shaped products (e.g. car parts).

2. Storage racking
With sturdy storage structures, storage racking is ideal to support a wide variety of goods.
Pallet racking
Pallet racking is designed to hold heavy and bulky items, such as bags of cement, furniture, household appliances, tyres, etc. Pallet racks can be supplied with fixed or removable boards for easy access to goods.

Push-Back Racking
Only one loading aisle provides high density storage, Push-Back Racking reduces forklift travel. The first pallets to be loaded are pushed back into the racking by the subsequent pallets. A FILO (first-in, last-out) system.

Pallet Flow Live Racking
Pallets are placed on powered remote controlled lifting shuttles that take pallets deep into the racking system. A high-density storage system that will bring pallets to the front when required.

3. Automated systems
Automation is becoming increasingly common in modern warehouses. It offers companies efficient stock management and considerable space savings. Such innovation comes in the form of three automated devices that are widely used in warehouses.
Vertical carousels
Vertical carousels consist of circular shelves rotating around a vertical axis. The products are stored in containers or trays that move up and down towards the operator. Carousel storage is particularly suitable for small parts such as electronic components.
Conveyors
Conveyors transport goods from one point to another without human intervention. They can either move single objects or batches containing a large number of products. Integrated into an automated sorting system, conveyors have the ability to select items based on their destination.
Robotisation
Robotic devices handle products directly by automatically moving and storing them. This technology is particularly suited to large warehouses, often in the form of articulated arms, automated carts or drones.
4. Storage for specific products
Depending on the type of goods, it is sometimes necessary to use specific storage systems.
Compartment Cupboards
Storage cabinets are compact elements that allow the storage of small items before they are sold (e.g. electronic components).
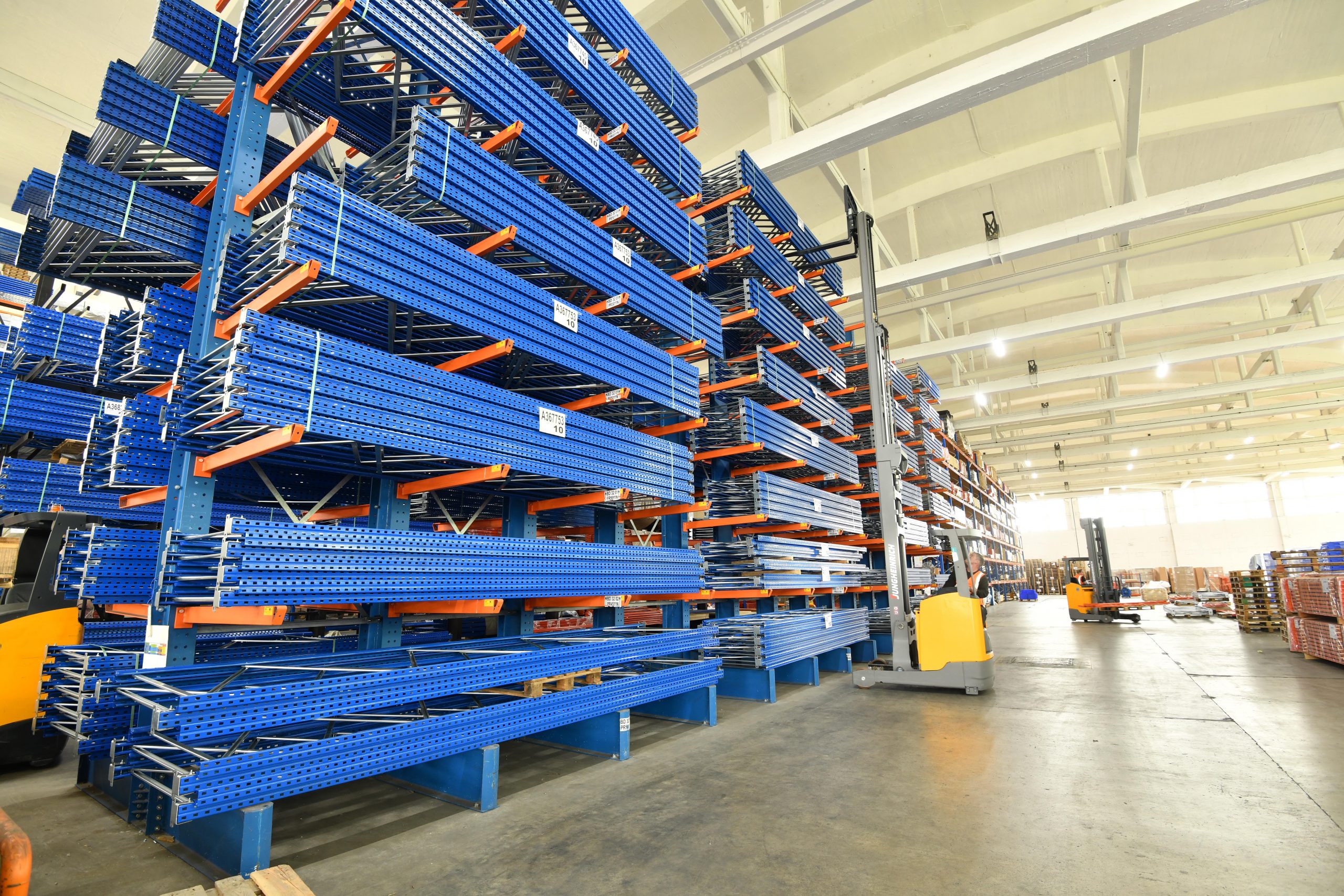
Cantilever racking
Using cantilever arm, this storage system is designed to carry loads horizontally. Widely used in the construction industry, cantilever racking is suitable for long and bulky products such as pipes, metal bars or boards.

Mezzanine Floors
Mezzanine floors increase the storage area by creating an additional level in the warehouse. They can store bulky items such as machinery or production equipment, for example.

Criteria for choosing the right type of storage for warehouses
There are several factors that should determine your choice of warehouse storage system.
The nature of the items stored
Some items require special storage conditions, such as a controlled temperature or a specific humidity level. Therefore, it is important to choose a storage system that takes into account the nature of the stored items, so they won’t deteriorate.
Size and weight of products
The option chosen must be able to support the weight and size of the items stored. Pallet racking is suitable for heavy and bulky items, while planks are more suitable for light items.
Stock turnover
If items have a high stock turnover, a storage system that allows quick and easy access is needed. In this case, mobile shelving or gravity racking seem ideal. Conversely, if the turnover is low, a more compact solution such as pallet racking is suitable.
The space available
It is important to select a storage system that maximises the space available in the warehouse. For example, pallet racking enables operators to vertically stock products, and mobile shelving moves the goods sideways.
Capital and operating costs
Some storage systems are more expensive than others. However, they can offer significant advantages. If a system ensures rapid retrieval of items or has a very high storage capacity, costs can be reduced in the long term.
The different types of storage provide many solutions to meet the specific needs of each company. Among them, technological developments represent a real asset for stock management. It is still important to select the appropriate storage system to ensure optimal warehouse management, productivity and profitability. Looking to optimise your storage and replenishment strategy? Download our “Guide to inventory management” white paper for more information.